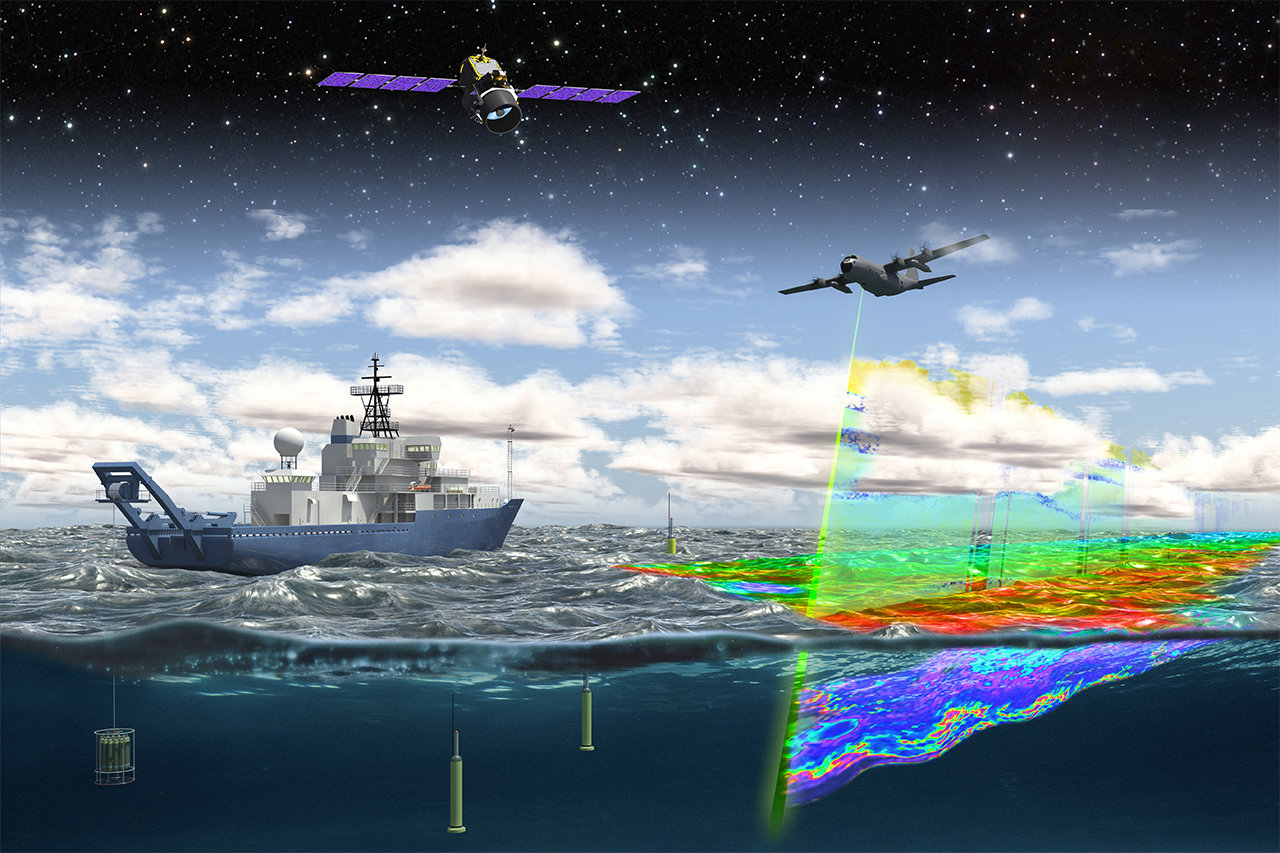
NASA ocean research is an exciting field that bridges space exploration with the mysteries of Earth's waters. Many people think of NASA as solely focused on space, but its work extends to understanding our own planet, especially its vast oceans. Through cutting-edge technology and global partnerships, NASA plays a crucial role in studying marine ecosystems, climate change impacts, and the health of our oceans.
Our oceans cover more than 70% of Earth's surface, yet much of their depths remain unexplored. NASA's ocean research initiatives aim to change that by using satellites, remote sensing, and advanced data analytics to monitor and analyze the world's oceans. This research provides critical insights into how our planet's climate is changing and how these changes affect marine life and human communities.
As we delve deeper into this article, you'll discover how NASA's ocean research contributes to global knowledge about our planet's water systems. From monitoring sea level rise to studying ocean currents and marine biodiversity, NASA's efforts are pivotal in addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
Read also:Jigga Boo Unveiling The Mystery Behind The Viral Sensation
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- NASA Satellites and Ocean Monitoring
- Impact of Climate Change on Oceans
- Marine Biodiversity and Conservation
- Sea Level Rise and Coastal Communities
- Advanced Technology in Ocean Research
- Global Partnerships and Collaborations
- Data Collection and Analysis
- Future Directions in Ocean Research
- Conclusion and Call to Action
NASA Satellites and Ocean Monitoring
Satellite Technology
NASA employs a fleet of satellites to monitor Earth's oceans, providing valuable data on sea surface temperature, salinity, and currents. These satellites, such as the Jason series and Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, are equipped with advanced sensors that can measure ocean conditions from space with remarkable accuracy.
For instance, the Jason-3 satellite tracks sea level changes, helping scientists understand the long-term trends of global warming. By analyzing this data, researchers can predict future changes in ocean levels and their potential impacts on coastal regions.
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is another critical tool used in NASA ocean research. This technology allows scientists to gather information about the ocean without direct contact. Remote sensing instruments aboard satellites can detect chlorophyll concentrations, which indicate the presence of phytoplankton, the foundation of the marine food web.
- Satellites like MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) provide detailed images of ocean color, revealing areas of high biological activity.
- These images help scientists monitor the health of marine ecosystems and identify potential threats such as harmful algal blooms.
Impact of Climate Change on Oceans
Ocean Warming
One of the most significant effects of climate change on oceans is the increase in water temperature. NASA's research shows that the upper layers of the ocean have been warming steadily over the past few decades. This warming has far-reaching consequences, including the bleaching of coral reefs and the migration of marine species to cooler waters.
Data from NASA's satellites reveal that ocean warming is not uniform across the globe. Some regions, such as the Arctic, are experiencing more rapid temperature increases, leading to the melting of sea ice and the disruption of local ecosystems.
Acidification
Ocean acidification is another pressing issue caused by climate change. As the ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, its pH level decreases, making it more acidic. This change in chemistry affects marine organisms, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals and shellfish.
Read also:What Is Lil Uzi Vert Net Worth A Comprehensive Guide To The Rappers Wealth
NASA's research highlights the importance of monitoring ocean acidification to understand its impact on marine biodiversity and fisheries. By combining satellite data with in-situ measurements, scientists can create models that predict future changes in ocean chemistry.
Marine Biodiversity and Conservation
Biodiversity Hotspots
NASA's ocean research also focuses on identifying and protecting biodiversity hotspots—areas of the ocean with exceptionally high levels of species diversity. These regions are crucial for maintaining the health of marine ecosystems and supporting global fisheries.
Using satellite data, researchers can map these hotspots and track changes in their distribution over time. This information is vital for developing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the sustainable use of marine resources.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are strengthened by NASA's contributions to understanding marine ecosystems. The agency collaborates with international organizations and governments to implement policies that protect endangered species and preserve critical habitats.
For example, NASA's data on sea surface temperature and chlorophyll concentrations help identify areas suitable for marine protected areas (MPAs). These MPAs serve as safe havens for marine life, allowing populations to recover and thrive.
Sea Level Rise and Coastal Communities
Rising Sea Levels
Sea level rise is one of the most visible impacts of climate change, and NASA plays a key role in monitoring this phenomenon. Through its satellites and ground-based measurements, the agency provides accurate data on how quickly sea levels are rising and which regions are most at risk.
Studies conducted by NASA indicate that sea levels have risen by about 8-9 inches since 1880, with the rate of increase accelerating in recent years. This rise poses significant threats to coastal communities, including increased flooding, erosion, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater supplies.
Adaptation Strategies
To address the challenges posed by rising sea levels, NASA works with local governments and communities to develop adaptation strategies. These strategies may include building sea walls, restoring wetlands, and relocating infrastructure to higher ground.
By providing scientific data and modeling tools, NASA helps decision-makers plan for the future and mitigate the impacts of sea level rise on vulnerable populations.
Advanced Technology in Ocean Research
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
In addition to satellites, NASA uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to gather data on ocean conditions. These drones can fly over remote areas of the ocean, collecting information on wave patterns, wind speed, and sea surface temperature.
UAVs are particularly useful for studying areas that are difficult to access by traditional means, such as polar regions or areas affected by storms. Their ability to cover large areas quickly makes them an invaluable tool for ocean research.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs)
Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) are another technological advancement used in NASA ocean research. These robots can dive deep into the ocean, collecting data on water chemistry, marine life, and geological formations.
By deploying AUVs, scientists can explore the ocean's depths without the need for manned submersibles, reducing costs and increasing the scope of research. AUVs are equipped with sensors and cameras that provide high-resolution images and detailed measurements of the underwater environment.
Global Partnerships and Collaborations
International Cooperation
NASA's ocean research is a collaborative effort involving scientists and organizations from around the world. Through partnerships with agencies such as the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), NASA shares data and resources to enhance global understanding of ocean processes.
These collaborations enable the development of comprehensive models that integrate data from multiple sources, providing a more complete picture of the Earth's ocean systems.
Public-Private Partnerships
In addition to international cooperation, NASA also engages in public-private partnerships to advance ocean research. These partnerships involve collaboration with private companies, universities, and non-profit organizations to develop new technologies and applications for ocean monitoring.
For example, NASA has worked with tech companies to create innovative software tools that allow researchers to visualize and analyze large datasets more efficiently. These tools help accelerate scientific discovery and improve decision-making processes.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data Integration
Data collection and analysis are at the heart of NASA's ocean research. The agency uses a variety of methods to gather data, including satellite observations, in-situ measurements, and computer modeling. By integrating data from these different sources, scientists can create a more comprehensive understanding of ocean processes.
Data integration also allows researchers to identify patterns and trends that might not be apparent from individual datasets. For example, combining satellite data on sea surface temperature with in-situ measurements of ocean currents can reveal insights into how these factors influence each other.
Data Sharing
NASA is committed to open data sharing, making its research findings freely available to the public and scientific community. This commitment ensures that researchers worldwide can access and utilize NASA's data to advance their own studies and contribute to global knowledge about the oceans.
Through platforms such as NASA's Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS), users can access a vast archive of ocean-related data. This resource supports a wide range of applications, from climate research to resource management.
Future Directions in Ocean Research
Emerging Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, NASA's ocean research will benefit from new innovations that enhance data collection and analysis capabilities. For example, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data processing.
Additionally, the development of new sensor technologies will allow for more detailed and precise measurements of ocean conditions. These advancements will enable scientists to tackle complex questions about the Earth's oceans and their role in the global climate system.
Long-Term Goals
NASA's long-term goals in ocean research include improving our understanding of the Earth's water cycle, predicting future changes in ocean conditions, and supporting sustainable management of marine resources.
To achieve these goals, NASA will continue to invest in cutting-edge technology and foster collaborations with global partners. By doing so, the agency aims to ensure that future generations inherit a healthy and thriving ocean ecosystem.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, NASA ocean research plays a vital role in advancing our understanding of Earth's oceans and their importance to the global climate system. Through its use of advanced technology, global partnerships, and commitment to data sharing, NASA is at the forefront of addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.
We invite you to take action by exploring NASA's resources and staying informed about the latest developments in ocean research. Share this article with others to spread awareness about the critical work being done to protect our planet's oceans. Together, we can make a difference in preserving the health and vitality of Earth's marine ecosystems for future generations.