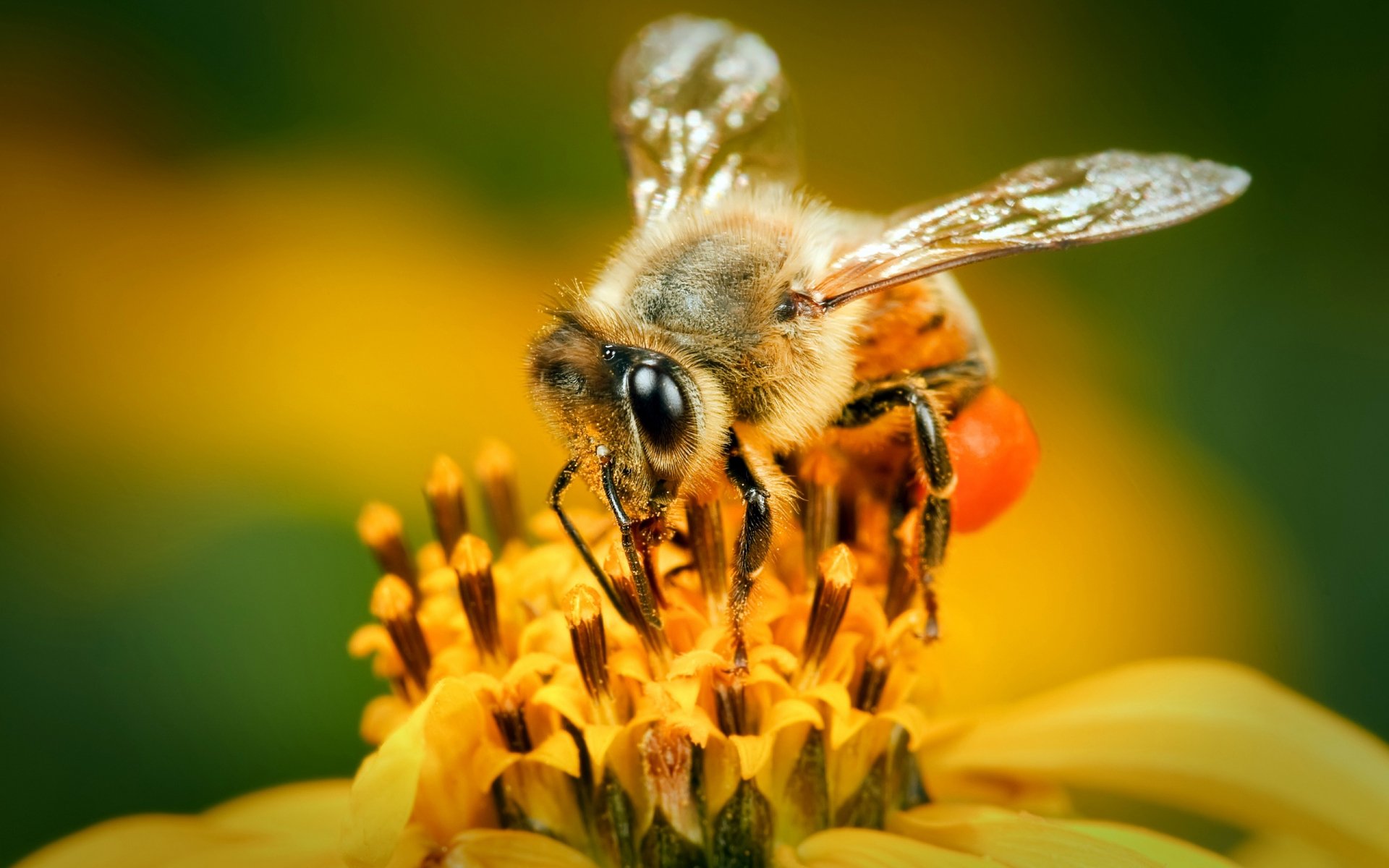
Bees are among the most important creatures on Earth, playing a crucial role in pollination and maintaining ecological balance. These tiny insects contribute significantly to global food production and biodiversity. Their activities ensure the survival of countless plant species and, by extension, the animals that depend on them. Understanding bees and their importance is essential for preserving the health of our planet.
Despite their small size, bees have a massive impact on the environment. They are responsible for pollinating about 75% of the world's flowering plants and nearly 35% of global food crops. This makes them indispensable for agricultural productivity and ecological sustainability. However, bee populations are declining at an alarming rate due to habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use.
This article explores the fascinating world of bees, their ecological significance, and the challenges they face. By delving into their biology, behavior, and contributions to the ecosystem, we aim to raise awareness about the importance of conserving these vital insects. Together, we can take action to protect bees and ensure a sustainable future for all living beings.
Read also:Regal Food Prices What You Need To Know In 2023
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Bees
- Biological Overview of Bees
- Types of Bees
- The Role of Bees in Pollination
- Bee Products and Their Uses
- Challenges Facing Bee Populations
- Conservation Efforts for Bees
- Interesting Facts About Bees
- Economic Impact of Bees
- Busting Common Bee Myths
- Conclusion
Introduction to Bees
Bees belong to the superfamily Apoidea, which includes approximately 20,000 species worldwide. These insects are primarily known for their role in pollination, a process that is critical for the reproduction of flowering plants. While honeybees are the most famous, there are many other bee species, each with unique characteristics and ecological roles.
Bees have been around for millions of years, evolving alongside plants to form symbiotic relationships. Their ability to transfer pollen between flowers ensures genetic diversity in plant populations, leading to healthier ecosystems. This relationship is vital for both wild plants and cultivated crops, making bees an essential component of global agriculture.
Unfortunately, human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and pesticide use threaten bee populations. Understanding the biology and behavior of bees is the first step toward addressing these challenges and safeguarding their survival.
Biological Overview of Bees
Physical Characteristics
Bees are small to medium-sized insects with three main body parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen. They have six legs, two pairs of wings, and a pair of antennae used for sensing their environment. Most bees are covered in fine hairs, which help them collect pollen during foraging.
Their bodies are adapted for efficient pollination, with specialized structures such as pollen baskets on their legs and a long proboscis for reaching nectar deep within flowers. These physical traits enable bees to perform their ecological functions effectively.
Social Structure
While some bee species are solitary, others live in highly organized colonies. Honeybees, for example, are social insects that live in hives with thousands of individuals. A typical colony consists of a queen bee, worker bees, and drones. Each member has specific roles and responsibilities, contributing to the colony's survival and success.
Read also:Capricorn And Pisces A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Their Compatibility
Solitary bees, on the other hand, do not live in colonies. Instead, they build individual nests and care for their offspring independently. Despite their solitary nature, these bees are still important pollinators and contribute significantly to ecosystem health.
Types of Bees
There are several types of bees, each with distinct characteristics and ecological roles. Below are some of the most common bee species:
- Honeybees: Known for producing honey and living in large colonies.
- Bumblebees: Large, fuzzy bees that are excellent pollinators of crops and wild plants.
- Carpenter Bees: Solitary bees that burrow into wood to create nests.
- Mason Bees: Solitary bees that use mud to construct their nests.
- Sweat Bees: Small bees that are attracted to human sweat and are important pollinators of wildflowers.
The Role of Bees in Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the male parts of a flower to the female parts, enabling fertilization and seed production. Bees are one of the primary pollinators, responsible for pollinating a wide variety of plants, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and wildflowers.
When bees visit flowers to collect nectar and pollen, they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another. This process increases the chances of successful fertilization and seed production, leading to higher crop yields and greater biodiversity. Without bees, many plant species would struggle to reproduce, resulting in a decline in food availability for both humans and wildlife.
Bee Products and Their Uses
Honey
Honey is one of the most well-known products of bees. It is produced by honeybees from the nectar of flowers and is valued for its sweetness and nutritional benefits. Honey has been used for centuries as a natural sweetener and is also known for its antimicrobial properties.
Beeswax
Beeswax is another valuable product of bees, used in a variety of applications such as candles, cosmetics, and polishes. It is produced by worker bees to construct the honeycomb within their hives.
Pollen
Pollen collected by bees is rich in nutrients and is often consumed as a dietary supplement. It is believed to boost immunity, improve digestion, and enhance overall health.
Challenges Facing Bee Populations
Bee populations are facing numerous threats that endanger their survival. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture expansion reduces the availability of nesting sites and food sources for bees. Pesticides, particularly neonicotinoids, have been linked to bee mortality and colony collapse disorder (CCD).
Climate change also poses a significant threat to bees, as it alters flowering patterns and disrupts the synchronization between bees and plants. Diseases and parasites, such as the Varroa mite, further exacerbate the challenges faced by bee populations.
Conservation Efforts for Bees
Efforts to protect bees involve a combination of policy changes, scientific research, and public awareness campaigns. Governments and organizations are working to reduce pesticide use, restore habitats, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Individuals can also contribute to bee conservation by planting bee-friendly gardens, avoiding pesticide use, and supporting local beekeepers. Educating others about the importance of bees and advocating for their protection can help ensure their survival for future generations.
Interesting Facts About Bees
- Bees have been producing honey for over 150 million years.
- A single honeybee can visit up to 5,000 flowers in a day.
- Bee dances, such as the waggle dance, are used to communicate the location of food sources to other bees.
- Bees are the only insects that produce food consumed by humans.
- Honey never spoils and has been found in ancient Egyptian tombs, still edible after thousands of years.
Economic Impact of Bees
The economic value of bees cannot be overstated. According to a study published in the journal Ecological Economics, bees contribute approximately $235 billion to the global economy through pollination services alone. This figure underscores the importance of bees to agriculture and food security.
In addition to their role in pollination, bees also support industries such as apiculture, which involves the commercial production of honey and other bee products. These industries provide livelihoods for millions of people worldwide and contribute significantly to local economies.
Busting Common Bee Myths
There are many misconceptions about bees that can hinder efforts to protect them. Below are some common myths and the truth behind them:
- Myth: All bees sting. Truth: Only female bees have stingers, and not all species are aggressive.
- Myth: Bees are dangerous. Truth: Bees are generally harmless and only sting when they feel threatened.
- Myth: Bees are only important for honey production. Truth: Bees play a vital role in pollination and ecosystem health.
Conclusion
Bees are indispensable to the health of our planet, playing a crucial role in pollination and maintaining ecological balance. Their contributions to global food production and biodiversity make them vital for the survival of countless species, including humans. However, bee populations are under threat from habitat loss, pesticide use, and climate change.
To protect bees and ensure their survival, we must take collective action. This includes reducing pesticide use, restoring habitats, and promoting sustainable practices. By raising awareness about the importance of bees and supporting conservation efforts, we can help preserve these incredible insects for future generations.
We invite you to share this article with others and join the movement to protect bees. Together, we can make a difference and ensure a sustainable future for all living beings. For more information on bees and their conservation, explore our other articles and resources.